[ Opisthokonta | Metazoa | Eumetazoa | . . .
. . . | Ancylostomatidae | Ancylostomatinae | Ancylostoma ]
 Picture Source
Picture Source
|
| Taxonomy: | Eukaryota | Opisthokonta | Metazoa | Eumetazoa | Bilateria | Protostomia | Ecdysozoa | Nematoda | Chromadorea | Strongylida | Ancylostomatoidea | Ancylostomatidae | Ancylostomatinae | Ancylostoma |
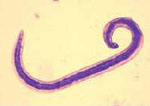
| Comment: | Many species of hookworms (Families: Ancylostomatidae and Uncinariidae) are known to infect carnivores and ruminants including dogs, cats, foxes, wolves, swine, cattle, sheep, goats, alpaca, llama, deer, seals, and elephants. A.caninum and infect dogs and cats respectively. Ancylostoma duodenale and Necator americanus are common human hookworms. Infection by human hookworm is through the skin usually the feet or hands. After penetration infective larvae migrate through the body to the small intestine where they reach sexual maturity. Attachment of hookworms to the small intestine of a host where they suck blood results in hemorrhages and anemia. |
|
|
|
Go to NCBI Taxonomy (51022) |
|
|
|  |
Encyclopedia of life |
|
|  |
Wikipedia |
Genome files
|
 Picture Source
Picture Source
 Picture Source
Picture Source